In chemistry hydrophosphonylation refers to any reaction where addition across a double bond generates a phosphonate (RP(O)(OR')2) group. Examples include the Kabachnik–Fields reaction, where a dialkylphosphite reacts across an imine to form an aminophosphonate. The reaction is catalyzed by bases and is subject to organocatalysis. Important compounds generated by this reaction include the common herbicide glyphosate.
Hydrophosphonylation reactions
- Kabachnik–Fields reaction
- Pudovik reaction
- Abramov reaction
See also
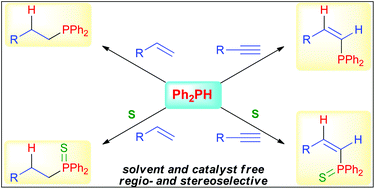
- Hydrophosphination - the addition of a phosphine derivative (PHR2) across a double bond
References