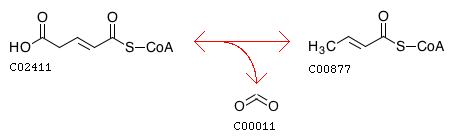
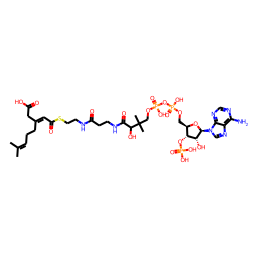
Glutaconyl-CoA is an intermediate in the metabolism of lysine. It is an organic compound containing a coenzyme substructure, which classifies it as a fatty ester lipid molecule. Being a lipid makes the molecule hydrophobic, which makes it insoluble in water. The molecule has a molecular formula of C26H40N7O19P3S, and a molecular weight 879.62 grams per mole.
Glutaconyl-CoA is postulated to be the main toxin in glutaric aciduria type 1. In certain fermentative bacteria, glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylation is catalyzed by a Na -dependent decarboxylase (EC 7.2.4.5) and is coupled with Na ion translocation, which creates a sodium-motive force as an alternate energy source for these organisms.
See also
- Glutaconate CoA-transferase
- Glutaconyl-CoA decarboxylase
References